The viral documentary traces China’s unregulated mining industry, and the health and safety risks that haunt it—and the director’s own family
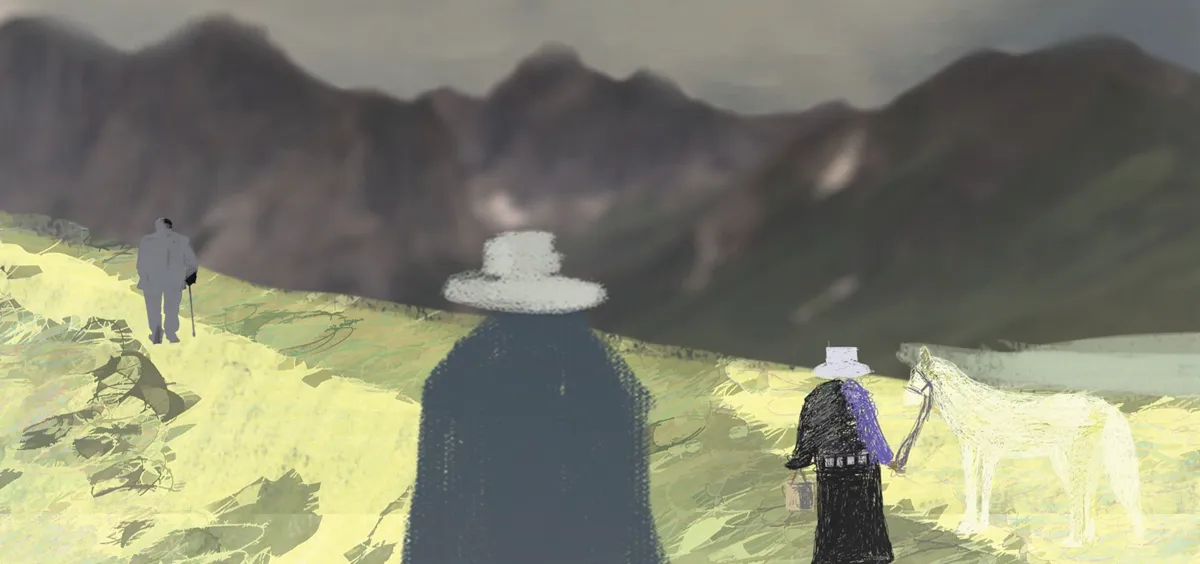
Three hours before sunrise, hostler Jiang Meilin straps white sacks of supplies onto the saddle, and prepares to head up to the coal mines. “No explosives today; there’s an inspection,” he explains to the camera.
In the opening sequence of Miners, the Horsekeeper, and Pneumoconiosis, filmmaker Jiang Nengjie follows the horse caravan up the Yuechengling Mountains in southwestern Hunan province, whose inhabitants are said to have mined the ore-rich landscape since the end of the Qing dynasty. In the distance, explosions sound from coal mines said to be over a thousand meters deep. Local officials are bribed to give warnings before safety inspections, so it’s business as usual in a rural industry that is as popular as it is informal, illegal, and dangerous.
Filmed intermittently between 2010 and 2018, Jiang’s documentary is a chronicle of the rise and fall of illegal coal mining in his hometown, and the sweep of lung diseases that accompanied it. With their lungs hardened by long-term inhalation of dust, miners cough and hack to their deaths before Jiang’s camera while struggling to receive medical treatment. Nationwide, civil organizations estimate that 6 million people suffer from pneumoconiosis, informally known as “black lung,” making it China’s number one occupational disease.
In a genre typically glutted with glossy state TV productions, full of sweeping drone shots and narrated with poetic speech, Jiang’s documentary strives for a level of candor that CCTV crews rarely reach. The film is unsentimental, honest, unnarrated, but sharply observational, allowing the lives of miners to quietly unfold to the soundtrack of casual chatter, impulsively belted country songs, and restrained emotion in Hunan dialect.
The presence of the camera is remarkably unobtrusive, at times even the butt of the jokes which the workers throw out as Jiang walks into the illegal mine. Unlike the usual ossifying distance between filmmaker and subject, the documentary’s scintillating brutality comes from the fact that the community recognizes Jiang intimately as their own. In interviews with media, Jiang has revealed that the hostler is his father, and the illegal mine’s owner is his cousin.

Zhao Pinfeng (center) passed away from lung disease in 2018
Jiang’s family has also been scarred by the industry: His grandfather died of a mining accident when Jiang was 7 years old at the same site where Jiang shoots, and his father and two of his uncles have all contracted pneumoconiosis.
Structured in three parts, the film begins by portraying the harsh lives of miners on the mountain. It then follows the workers back to the village when the mine closes in 2013, after Jiang’s cousin goes bankrupt in order to compensate the family of a miner injured in an accident. It’s a compassionate act, as the contract-less job leaves laborers little legal basis to demand compensation for occupational injury. After the closure, Jiang’s cousin moves to Changsha to work in food delivery.
The final section, with a clear upgrade in image quality, begins in 2016 when Jiang’s father pays a visit to Zhao Pinfeng, a former workmate in a neighboring village. Having worked in mines since he was 15 years old, Zhao, in his 40s, is diagnosed with terminal pneumoconiosis, unable to work, and has to provide for a wife with intellectual disabilities and two school-aged children. Over the next three years, Jiang follows the family’s struggle to receive medical treatment and social compensation.
Most scathing is Jiang’s depiction of the village’s official poverty alleviation program, whose promises are hollowed out by local corruption. When Zhao applies to the village leaders for a basic living allowance, they ask for many documents, and finally give him an allowance that won’t cover his hospital fees. “If only there were journalists to come to our village,” an elderly villager muses from a stool outside. Another responds, “Useless. Journalists need approval. They can only report good news.”
At town meetings, one villager recounts, they’re told how to answer questionnaires from higher-up authorities: “What do you think of policemen? Are you satisfied with the court?” If they mark all as 10, leaving one 9, they can get a 200 RMB reward from the local government. “What the hell is this?” says the old man, rocking in his chair.
The villagers’ anger is Jiang’s own. Determined for the stories from his village to circulate as widely as possible, Jiang made the film free to watch; users who marked it as “Want to Watch” on review app Douban allegedly received a private message from Jiang with a link to watch the film, which could also be obtained by adding the filmmaker on WeChat. Baidu Drive has also released a public download link in support of the film. Many viewers have sent the filmmaker a voluntary donation on WeChat as their movie “ticket,” and the film dominated the “Top Word-of-Mouth Film” list on Douban for several weeks.
For Jiang, documentary filmmaking is a necessity. In times that he couldn’t afford to film, he took care of horses alongside his father, earning as little as 100 RMB a day. “I don’t care about cost recovery,” Jiang wrote on Douban. “As a low-income person from a rural background, I have seen too many such absurd scenes,” he elaborated in an interview with Vista magazine. “If one day I am no longer angry and choose to accept reality frankly, I probably won’t make documentaries.”
MUST-SEE MOVIES AND SERIES
China’s Battle Against Covid-19
This 28-minute English-language documentary was released in early April on Tencent Video, Bilibili, and Youtube, offering a brief look into China’s fight against the pandemic. Featuring interviews with international scholars, foreign medical personnel in China, Chinese residents, and volunteer doctors in Wuhan, the film presents itself as an effort to give China’s side of the story amid rumors and accusations. It takes the audience through the discovery of the virus, China’s response, the transportation shutdown in Wuhan, support from the international community, and the impact on trade.
The Winners
In this lighthearted comedy, bank employee Yan Jin (Dong Chengpeng) annoys his boss and colleagues with his strict and meticulous attitude toward work. When he is assigned to play a bank robber in a company drill, everyone tells him it’s just a formality, and he is supposed to go quietly with the police when “captured.” But under his Pikachu head mask, the deadly serious Yan is formulating an elaborate plan. This parody of a classic heist film is one of the few new movies released in the age of social distancing, and is available to view online for free on Xigua Video.
Real Estate Agents
Dishonest. Scammers. Complicated. These are the responses people typically give when asked for their impression of real estate agents. Though seemingly lurking on every street corner, the besuited workers of this fast-changing industry reveal their side of the story for the first time in this six-episode documentary series. Available on Tencent Video, each 19-minute long episode focuses mainly on the experience of a single agent—out of 150 interviewed for the series—as they navigate the pressure to sign the first deal, the price of being honest in a shady market, and the general disdain society shows toward them.
Du Fu: China’s Greatest Poet
Written and presented by Michael Wood, BBC 4’s documentary on the renowned Tang poet follows Du Fu from birth to death. A young genius eager to serve his country, Du experienced setbacks in pursuing a career in government. Sir Ian McKellen recites translations of Du’s works as the poet experiences the descent of the once prosperous Tang into war and chaos, reflecting Du’s deeply rooted understanding of history, his sympathy for ordinary people, and his “cultural sorrow” at the decline of a once-great civilization. – Liu Jue (刘珏)
“Bated Breath” is a story from our issue, “Contagion”. To read the entire issue, become a subscriber and receive the full magazine. Alternatively, you can purchase the digital version from the iTunes Store.